Михайло Зборовський Космобет гравці “зумери”, діалог про відповідальність
September 11, 2023Sober Living vs Halfway House: What’s the Difference?
October 18, 2023Use GROUPBY with Multiple Tables in Excel for Better Analysis
Also known as the vertical percentage analysis, you can then use this to evaluate company performance and compare it with previous results to understand the direction of your company. For example, a company may have significant one-time expenses or revenues that distort the overall picture when viewed purely in percentage terms. Standardizing financial statements as percentages through vertical analysis helps make comparisons regardless of absolute size differences. Trends in the percentages highlight comparative strengths and weaknesses between companies. On an income statement for a company with Rs. 100 crores total revenue, if cost of goods sold was Rs. 60 crores and operating expenses were Rs. 20 crores, the vertical analysis percentages would be. To increase the effectiveness of vertical analysis, multiple year’s statements or reports can be compared, and comparative analysis of statements can be done.

Net Income
The information vertical analysis provided in the balance sheet provides the change in working capital, fixed income over some time. The same can be done with the income statement, where the previous years can be compared and find out the change in the working capital and fixed assets over time. Adaptability, a proactive approach, and a willingness to embrace change are essential.
Vertical vs. Horizontal Analysis

Vertical analysis of the income statement and balance sheet provides insights into the structural composition of revenues, expenses, assets and liabilities. On the income statement, seeing that cost of goods sold takes up 60% of total revenue while operating expenses takes up 20%, provides perspective on the expense structure needed to generate each rupee of revenue. Tracking changes in these percentages over time shows shifts in operational efficiency and costs. A 2019 McKinsey study found that top performing companies carefully manage the composition of expenses, keeping non-core costs below 15% of revenue.
What is Economic Profit and Why is it Important for Businesses?
Vertical analysis, also called common-size analysis, is all about looking at financial statements as percentages rather than absolute dollar amounts. This enables the user to quickly judge the relative size and importance of each line item. For example, on the income statement, expressing revenue as 100% and every expense item as a Insurance Accounting percentage of total revenue immediately shows which costs are highest and lowest relative to the company’s sales. In this example, total assets are taken as the base figure (100%), and each asset is then calculated as a percentage of total assets. Cash, for instance, makes up 15% of total assets, while equipment represents a significant 40%.
How to Calculate Vertical Analysis of the Income Statement

For example, comparing current expenses to previous years as a proportion of revenue is far more useful than looking just at the raw numbers. Quickly surface insights, drive strategic decisions, and help the business stay on track. Additionally, in all sectors of the economy, vertical analysis may help you understand how the relative percentages relate to the numbers and to one another.
- Vertical analysis is a method of financial statement analysis in which each line item is shown as a percentage of the base figure.
- If total assets were Rs. 500 crores, current assets were Rs. 150 crores, and fixed assets were Rs. 300 crores, the common size balance sheet would state as below.
- One of the most significant advantages of using GROUPBY with dynamic arrays is its ability to handle changes in your data automatically.
- Equity is shown to be 60% of total assets, indicating a strong equity position.
- For example, if a specific expense item is consistently increasing as a percentage of revenue, it may indicate a need to optimize costs or explore opportunities for expense reduction.

We can gather from the data below that the sales of the company increased consistently from year 1 to year 3. However, while sales rose consistently from year 1 to 3, net income dropped markedly in year 3 so we would like to look into this in more detail. Because we entered our costs and expenses as negatives, i.e. to reflect that those items are cash outflows, we must place a negative sign in front when applicable, so that the percentage shown is a positive figure. So if we had multiple years of historical data, it is recommended to organize the percentage calculations into a single section on the far right or below the financials with the timing of the periods aligned. Despite the various advantages, there are a few factors of vertical analysis accounting that prove to be a disadvantage.
When we carry out vertical analysis on the income statement, it shows the top-line sales figure as 100% and every other item is shown as percentage of the total sales for that year. Each item in the income statement is divided by the company’s total sales for that year (which gives us a common size income statement). Vertical analysis is a useful financial statement analysis technique that shows each line item on the income statement or balance sheet as a percentage of a base figure. This converts the raw financial data into standardized percentages allowing for an “apples-to-apples” comparison between different companies even if they have very different revenue figures or asset sizes. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk through the vertical analysis process with examples to show you exactly how to calculate vertical analysis for the income statement and balance sheet. On the balance sheet, vertical analysis displays the financing structure in terms of percentages of assets.
Vertical analysis in action: income statement insights
- Operating expenses account for 25% of the total revenue, resulting in an operating income of 35%.
- The key advantage of vertical analysis is improving comparability between companies.
- Our vertical analysis calculator is available to assist in carrying out the required calculations.
- Vertical analysis streamlines financial analysis, offering a clear and concise view of the most significant financial metrics.
- With Acterys, FP&A professionals can conduct thorough vertical analysis and make well-informed decisions thanks to its scenario planning and collaboration features.
- In the 3rd year, the COGS decreased compared to the previous years, and the income increased.
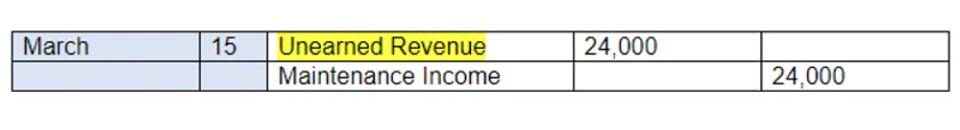
We can also view from this table that marketing expenses as a percentage of total sales increased to 8% as a percentage of total sales in year 3, compared to 6% in year 2. However, these two types of expenses did not really rise substantially and only account for a unearned revenue relatively small proportion of revenue. For example, in the income statement, each line item is shown as a percentage of revenue. This allows us to determine which cost or revenue item has the biggest impact on the overall financial performance.
